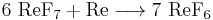Rhenium(VI) fluoride
| Rhenium(VI) fluoride | |
|---|---|
|
rhenium(VI) fluoride |
|
|
Other names
rhenium hexafluoride |
|
| Identifiers | |
| PubChem | 66231 |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | F6Re |
| Molar mass | 300.2 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow crystalline solid[1] |
| Density | 4.94g/mL[2] |
| Melting point |
18.5 °C[1] |
| Boiling point |
33.7 °C[1] |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Rhenium hexafluoride, also rhenium (VI) fluoride, (ReF6) is a compound of rhenium and fluorine and one of the sixteen known binary hexafluorides.
Contents |
Synthesis
Rhenium hexafluoride is made by combining rhenium heptafluoride with additional rhenium metal at 300 °C in a pressure vessel.[2]
Description
Rhenium hexafluoride is a liquid at room temperature. At 18.5 °C, it freezes into a yellow solid. The boiling point is 33.7 °C.[1]
The solid structure measured at −140 °C is orthorhombic space group Pnma. Lattice parameters are a = 941,7 Å, b = 8.570 Å, and c = 4.965 Å. There are four formula units (in this case, discrete molecules) per unit cell, giving a density of 4.94 g·cm−3.[2]
The ReF6 molecule itself (the form important for the liquid or gas phase) has octahedral molecular geometry, which has point group (Oh). The Re–F bond length is 1.823 Å.[2]
Use
Rhenium hexafluoride is a commercial material used in the electronics industry for depositing films of rhenium.[3]
References
- This article incorporates information from the German Wikipedia.
- ^ a b c d CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 90. Auflage, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 2009, ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0, Section 4, Physical Constants of Inorganic Compounds, p. 4-85.
- ^ a b c d T. Drews, J. Supeł, A. Hagenbach, K. Seppelt: "Solid State Molecular Structures of Transition Metal Hexafluorides", in: Inorganic Chemistry, 2006, 45 (9), S. 3782–3788; doi:10.1021/ic052029f; PMID 16634614.
- ^ doi:DOI: 10.1002/0471238961.1808051413051908.a01
This citation will be automatically completed in the next few minutes. You can jump the queue or expand by hand
Further reading
- Gmelins Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie, System Nr. 70, Rhenium, Part A, pp. 102–105.
External links
|
|||||